USSPS Codes
Code USSPS is used to describe sunspot groups.
Example:
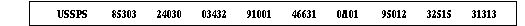
Definition of symbols:
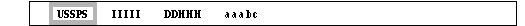
- USSPS comes from SunSPotS
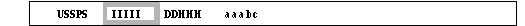
- I I I I I = station indicator
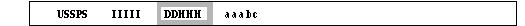
- DD = UT day of observation
- HHH = UT time of observation in hours and tenths of hour

- a a a = relative sunspot number
- b = seeing quality
- 1 = very poor
- 2 = poor
- 3 = fair
- 4 = good
- 5 = exceptional
- c = solar disk size used for measurement
- 1 = diameter of the solar disk less than 15 cm
- 2 = diameter of the solar disk between 15 and 30 cm
- 3 = diameter of the solar disk more than 30 cm
- 4 = individual sunspot groups at very high resolution

- d d = serial number of sunspot group
- AAA = area of sunspot group in tens of millionths of the solar hemisphere

- Q = quadrant (heliographic coordinates) in geometric center of sunspot groups is located
- 1 = NE (northeast)
- 2 = SE (southeast)
- 3 = SW (southwest)
- 4 = NW (northwest)
- XX = distance to the central meridian in degrees
- YY = heliographic latitude in degrees

- f = type of penumbra in the largest spot in group (Modified
Zurich (McIntosh) Sunspot Classification)
- 0 = no penumbra (Zurich class A or B)
- 1 = rudimentary (r)
- 2 = small symmetric (s) north to south diameter < 2.5°
- 3 = small asymmetric (a) north to south diameter < 2.5°
- 4 = large symmetric (h) north to south diameter > 2.5°
- 5 = large asymmetric (k) north to south diameter > 2.5°
- g = relative importance of the leading spot and density of the sunspot population
- 1 = leading spot largest and sunspot population density open
- 2 = following spot largest and sunspot population density open
- 3 = leading and following spots nearly same size and sunspot population density open
- 4 = leading spot largest and sunspot population density intermediate
- 5 = following spot largest and sunspot population density intermediate
- 6 = leading and following spot nearly same size and sunspot population density intermediate
- 7 = leading spot largest and sunspot population density compact
- 8 = following spot largest and sunspot population density compact
- 9 = leading and following spot nearly same size and sunspot population density compact
Note: g = / (slant line) for unipolar spots of Zurich class A, H or J
- h = Zurich or McIntosh modified sunspot class
- 1 = A
- 2 = B
- 3 = C
- 4 = D
- 5 = E
- 6 = F
- 7 = G
- 8 = H
- 9 = J
Note: If the above McIntosh f and g subtypes are given, for consistency with the Modified Zurich (McIntosh) Sunspot Classification, G and J types should then not be used. Normally G will be encoded as an open E or F and J will be encoded as a small H.
- ii = Number of spots in the group
